| PM上午场 | PM下午场 |
2020年12月ACCA考季第三天考试下午场结束了!各位参加ACCA-PM考试的考生们,你们都考了哪些知识点呀!快来看看网校的其他考生们在考试中都考了哪些知识点,看看有没有和你一样的!

持续更新>>>
转移定价:
转移定价(transfer price)知识点在ACCA历年考试中频率很高。一般来说,简单的考核方式会给出一些条件让考生判断产品的外部需求是否已经满足,工厂是否已经满负荷运转,这些情况下应该选用可变成本还是市场价格来定价。
做这类题目的时候需要从集团利益的角度的出发,考虑部门之间应该采取内部购销还是各自从外部购入或对外销售。总之,做出的决策和制定的价格既要满足集团的利益又不能影响各部门的绩效考评。
下面我们来看一下2011年12月Q2这道例题,虽然年份比较久远,但是非常经典,难度也比较大,可以说考出了精髓。
Bath Co is a company specialising in the manufacture and sale of baths. Each bath consists of a main unit plus a set of bath fittings. The company is split into two divisions, A and B. Division A manufactures the bath and Division B manufactures sets of bath fittings. Currently, all of Division A’s sales are made externally. Division B, however, sells to Division A as well as to external customers. Both of the divisions are profit centres.
The following data is available for both divisions:


The transfer price charged by Division B to Division A was negotiated some years ago between the previous divisional managers, who have now both been replaced by new managers. Head Office only allows Division A to purchase its fittings from Division B, although the new manager of Division A believes that he could obtain fittings of the same quality and appearance for $65 per set, if he was given the autonomy to purchase from outside the company. Division B makes no cost savings from supplying internally to Division A rather than selling externally.
Required:
(a) Under the current transfer pricing system, prepare a profit statement showing the profit for each of the divisions and for Bath Co as a whole. Your sales and costs figures should be split into external sales and inter-divisional transfers, where appropriate. (6 marks)
(b) Head Office is considering changing the transfer pricing policy to ensure maximisation of company profits without demotivating either of the divisional managers. Division A will be given autonomy to buy from external suppliers and Division B to supply external customers in priority to supplying to Division A.
Calculate the maximum profit that could be earned by Bath Co if transfer pricing is optimised. (8 marks)
(c) Discuss the issues of encouraging divisional managers to take decisions in the interests of the company as a whole, where transfer pricing is used. Provide a reasoned recommendation of a policy Bath Co should adopt.
答案解析
首先,我们要明确题目中部门A和B分别代表什么角色。B是生产产品所用辅料的一方,A需要采购辅料来生产主要产品然后对外销售。B部门既销售给A又对外部销售。浏览题干是,我们需要注意Division A 数据中的Fitting from Division B 75美元这个金额,它对B来说是销售收入,而对A是采购成本。
Division B 的对外销售金额80。另一个重要信息点是Maximum annual production and sales of sets of fittings (units) 200,000,Maximum annual external demand for sets of fittings (units) 180,000,Maximum annual internal demand for sets of fittings (units) 80,000。
这句话的意思是满足内外部总需求的产能是200,000个单位。A部门需求80,000,而外部需求是180,000,我们需要考虑先对外销售还是内部转移。如果优先满足内部需求80,000,那么只能对外销售120,000;如果先满足外部需求180,000,那么内部只能供应20,000。
接下来我们先看一下官方给出的答案:
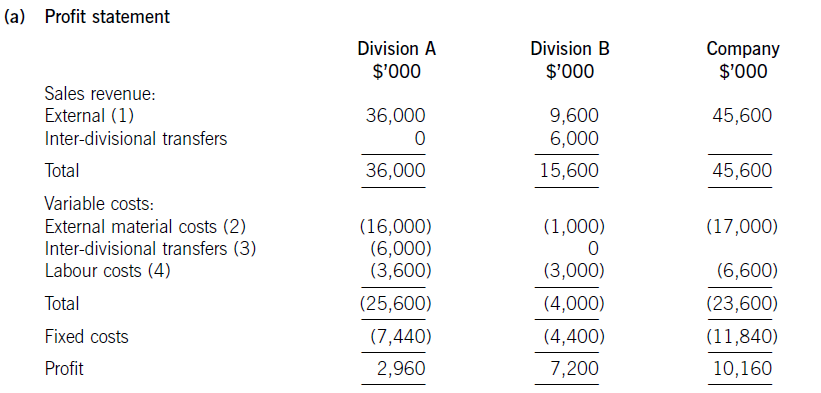
Workings ($’000)
(1)External sales
Div A: 80,000 x $450 = $36,000
Div B: 120,000 x $80 = $9,600
Div B: 80,000 x $75 = $6,000
题目中给出的信息是优先满足内部需求,所以先销售80,000给A部门,收入是80,000 x $75 = $6,000。剩下的产能(200,000-80,000=120,000)分配给外部市场,赚取的收入为120,000 x $80 = $9,600
(2)External material costs
Div A: 80,000 x $200 = $16,000
Div B: 200,000 x $5 = $1,000
(3)Inter-divisional transfers
Div A: 80,000 x $75 = $6,000
(4)Labour costs
Div A: 80,000 x $45 = $3,600
Div B: 200,000 x $15 = $3,000
ABC:
Activity based costing(ABC)作为完全成本法的一种代替会计核算方法受到了更多的青睐,因为它克服了传统方法带来的分配不公等问题。
随着制造业的不断发展,制造过程已逐渐从手工制造变为了机械制作,这代表了人工制造的比例在不断缩小,直至现在有的工厂可能已经出现全场只在关键环节才出现人工的控制,其他生产制造环节全都是通过机械来完成。
这样的现象如果再采用通过Labour hours来分配Overheads的话,就会产生产量高的部分分配到了较多的成本,产量低的部分被分配到比较少的成本,在成了明显的不公平。
ABC的出现就扭转了这样的局面。作业成本法把Overheads进行了细分,利用成本动因的分配方式来分摊费用则更为合理。
所谓成本动因就是追根溯源,看看到底是因为什么原因才使这项成本发生,之后再采用每个产品所消耗该资源的比例然后进行成本的分摊,打破了传统成本法分配标准单一且不符合实际的状态。
一个比较完成的作业成本法系统主要表现为以下三个步骤:
①Identify an organization’s major activities that support the manufacture of the organization’s products or the provision of its services.
②Use cost allocation and apportionment methods to charge overhead costs to each of these activities. The costs that accumulate for each activity cost centre is called a cost pool.
③Identify the factors which determine the size of the costs of an activity/affect the costs of an activity. These are known as cost drivers.
即使是再先进的方法还是有其弊端,针对于ABC这种比较高级的会计核算方法来说,不管是计算起来比较难把握,因为不是每种Overheads都可以被单一的Cost driver来分摊.
所以这样就造成不好计算的局面,还有在实施ABC之前的准备工作也比较复杂,要把成本按照成本动因分开就需要很大的工作量,很有可能采用ABC的成本大于其带来的好处。
希望大家在考试中取得满意的成绩,前程似锦。山高水远,江湖再见~希望大家都可以通过考试哟~
本内容由正保会计网校考生提供
网校教学团队整理

精品好课免费试听
